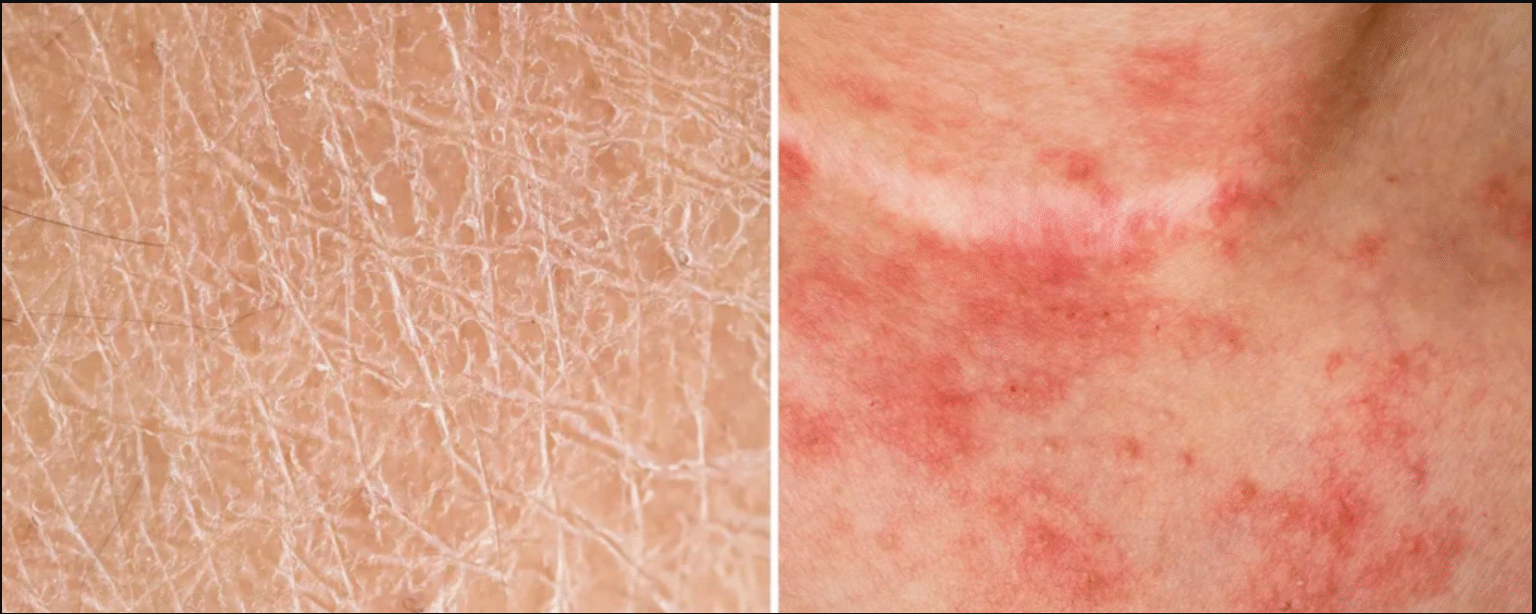
As temperatures drop and humidity decreases, many people notice their skin becoming dry, tight, or itchy. However, what often seems like simple dryness may actually be eczema—a chronic skin condition that requires medical care. Dermatologists emphasize that understanding the distinction between dry skin and eczema is essential for proper treatment and prevention.
Dry skin typically occurs when the skin loses its natural oils and moisture. It often appears as rough patches, flaking, or mild itching. Environmental factors, such as cold weather, strong winds, or the use of harsh soaps, can aggravate this condition. In most cases, dry skin is temporary and improves with consistent moisturization and gentle skin care.
Eczema, on the other hand, is a long-term skin disorder. It develops when the skin barrier is compromised, allowing allergens or irritants to trigger inflammation. The result is redness, swelling, and dry, cracked areas that can become intensely itchy. Eczema flare-ups may be caused by triggers such as allergens, emotional stress, or extreme weather changes. Unlike dry skin, eczema often requires prescribed creams and continuous medical management.
Expert Recommendations to Prevent Skin Dryness
Dermatologists recommend maintaining proper skin hydration during winter through a combination of internal and external care. Moisturizers play a crucial role in protecting the skin barrier. Experts suggest using oil-rich creams or lotions that contain hyaluronic acid and glycerine, which help retain moisture effectively.
In addition, hot showers should be avoided as they strip the skin of natural oils. Instead, use lukewarm water for bathing and gently pat the skin dry before applying moisturizer.
Hydration from within is equally important. Drinking enough water throughout the day supports the skin’s ability to stay supple and balanced. Experts also advise using mild, fragrance-free soaps to minimize irritation and prevent further dryness.
Managing Eczema with Care
For individuals suffering from eczema, dermatologists recommend consistent treatment under medical supervision. Applying gentle, fragrance-free emollients several times a day can soothe irritation and restore the skin barrier. Identifying personal triggers—such as certain detergents, fabrics, or foods—can help minimize flare-ups.
If redness, swelling, or severe itching persists, consulting a dermatologist is essential. They may prescribe anti-inflammatory creams or other medications to manage the condition effectively.
Recognizing whether your skin issue is simple dryness or eczema can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. While dry skin can often be resolved with proper moisturization and care, eczema requires ongoing attention and medical guidance.
Taking preventive measures, such as using the right moisturizer, avoiding hot water, and staying hydrated, can help maintain healthy, nourished skin throughout the cold season.